Not so long ago — through late February, say — the news about California’s “wet” season was how dry it had been. But that changed last month, when a series of late-season storms pulled the state back from the brink of a return to deep drought.
As the last March storm departed, I heard people asking, “Is that it? No more storms?”
But model-watchers saw a return to wet weather late this week, and those supercomputer prognostications have been borne out in the form of a very warm, very wet storm that is forecast to dump huge volumes of water over the northern two-thirds of the state.
One of the regions forecast to get the heaviest deluge is the Feather River watershed, above Oroville Dam and Lake Oroville. That’s news because the California Department of Water Resources, which owns and operates the dam, may be forced sometime in the next few days to release water down the dam’s half-completed spillway.
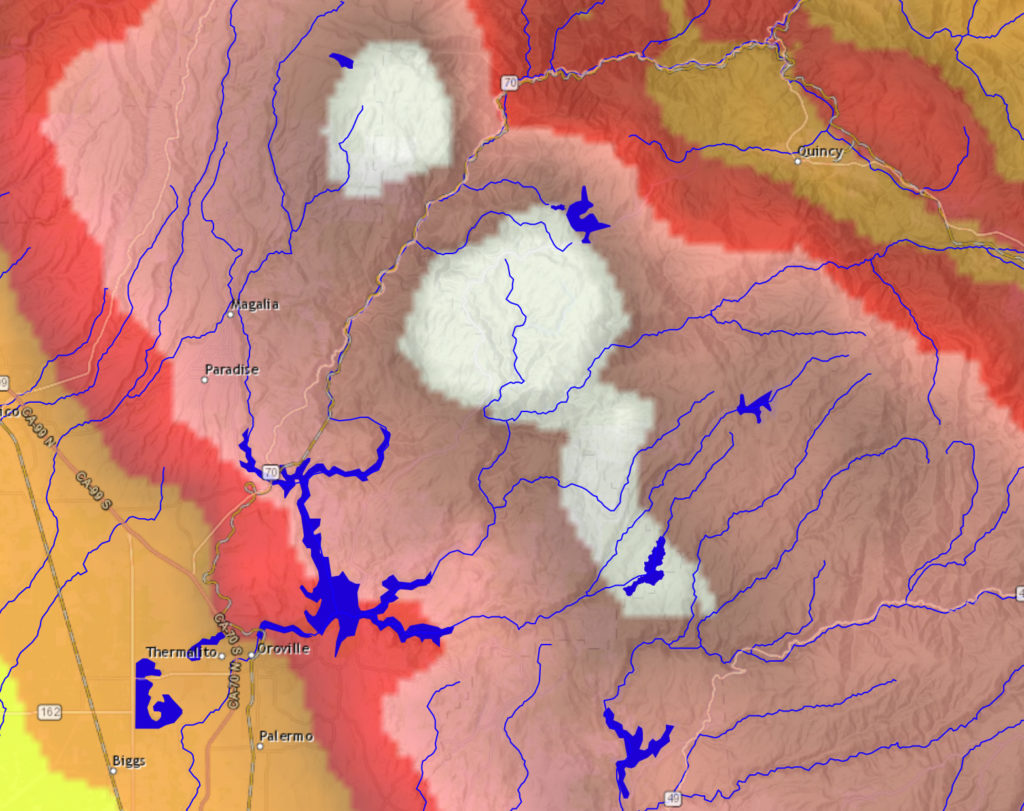
The image above is from the California-Nevada River Forecast Center, and it depicts a precipitation forecast for more than 7 inches of rain in parts of the Feather watershed over the next 72 hours. (There’s an interactive version of the map on the CNRFC site, here.) DWR has, without a doubt, modeled the expected runoff from that much rain falling so quickly, how fast the lake will rise, and when it will reach the “target” elevation at which the spillway gates will open and water will flow down the 3,000-foot-long concrete chute.
As of this morning, the reservoir is about 20 feet below the lip of the spillway inlet and about 37 feet below the target elevation of 830 feet above sea level. From outside, it’s hard to guess how quickly the lake might rise — that’s a function of the total precipitation, how saturated soils in the watershed are, how much snow might melt off in the watershed’s upper reaches, and how much water is released from the reservoir through the only currently available outlet, the dam’s hydroelectric plant. But given the rate of the lake’s rise during the last round of heavy rain, it would appear that it would be late next week before that 830 foot threshold is reached.
Here’s the current DWR statement on reservoir conditions and prospects for a spillway release.
