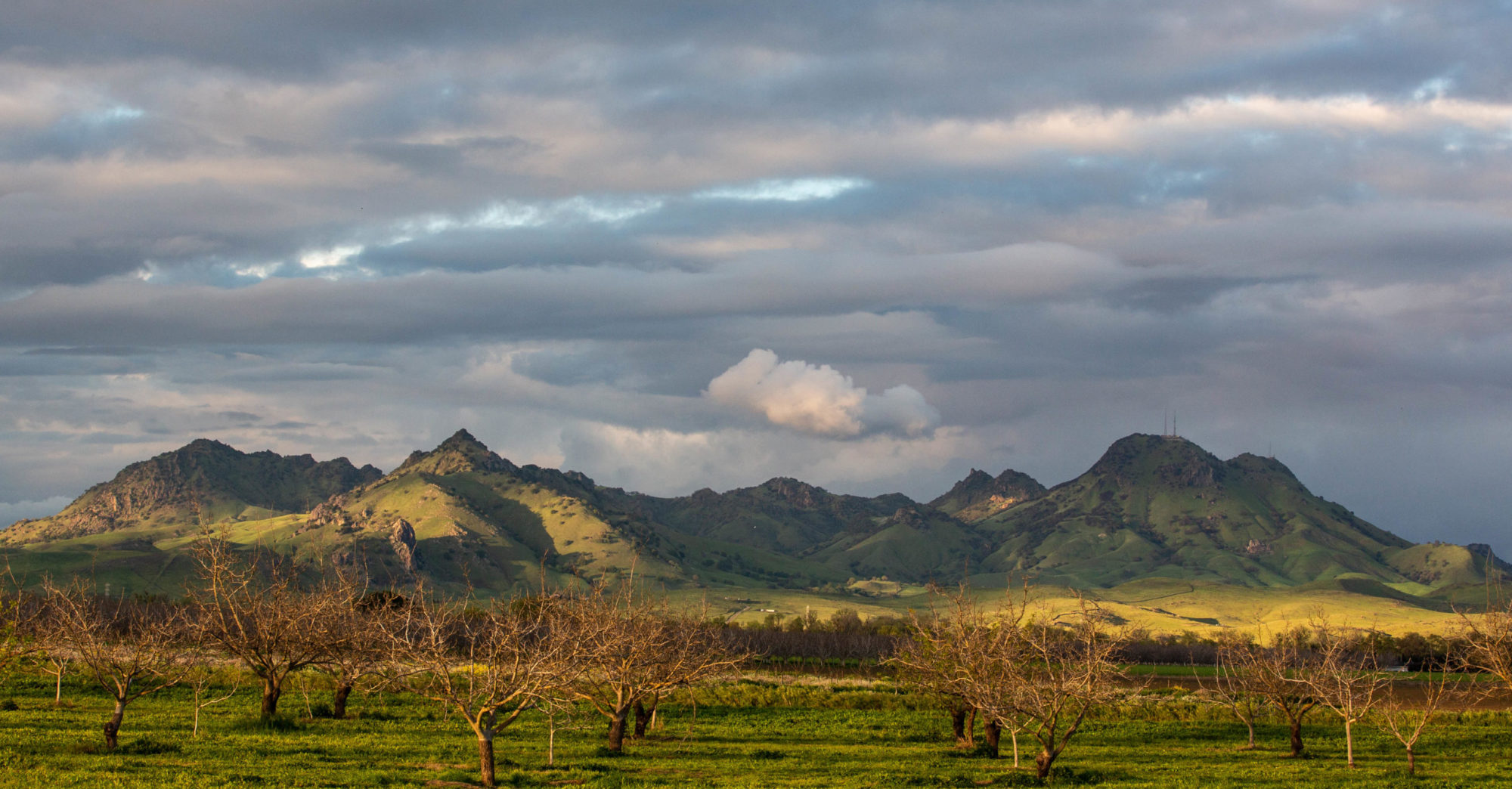
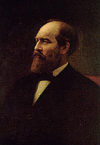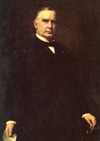Reading Minnesota Public Radio’s “Writer’s Almanac” today, I see a mention that today is the anniversary of the death, in 1881, of President James A. Garfield. Reading the item brings me face to face with the unpleasant truth that for years I’ve been spreading a spurious story about his death and in fact have confused certain details of Garfield’s assassination with the story of William McKinley‘s assassination 20 years later.
The story as I’ve told it: Garfield was visiting Buffalo. He was shot in the abdomen by a “disappointed office-seeker” (the stock phrase) as he passed through a train station. Emergency surgery was performed by the only available doctor, who turned out to be a veterinarian. Garfield appeared to be recovering from his wounds, which included a damaged intestine; but the vet’s botched work led to infection, gangrene, and a horribly protracted death nearly three months after he was shot.
The “Writer’s Almanac” version of events was at odds with my tale, so I was compelled to check my “facts.” I discovered my story is an amalgam of the Garfield-McKinley events, with one wholesale fabrication thrown in. So from checking a couple of reliable-looking Web resources (here and here), here are the key points in the long and painful demises of the two presidents.
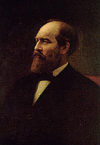 First, Garfield:
First, Garfield:
—On July 2, 1881, Garfield was leaving Washington, D.C., on a trip. While preparing to board a train, the “disappointed office-seeker” — actually a nut job with a .44-caliber revolver, Charles Guiteau — shot him twice. One bullet grazed Garfield, the other struck him in the back.
—Garfield was taken back to the White House and doctors summoned. Not a veterinarian in the pack. The physicians believed it was crucial to determine where the bullet was lodged and whether it had struck any vital organs. To do this, and a veterinarian would have done just as well, they began sticking their unwashed fingers and other probes into Garfield’s deep back wound to see if they could feel the slug or damaged organs. They kept at that effort for days or weeks without finding the bullet. Their patient was conscious for most of the poking and gouging and subsequent pus drainings.
—Despite initial optimism that Garfield would recover, the wound became infected, and the president died on Sept. 19, 1881, an astonishing and no doubt excruciating 80 days after he was shot.
—The most interesting detail of the efforts to treat Garfield is technological: At one point, Alexander Graham Bell was called in to use a metal detector he and aides had developed to try to find the bullet. The device was foiled, apparently, by a parallel innovation in sleep technology: The test was conducted while Garfield was lying on a mattress equipped with newfangled metal springs.
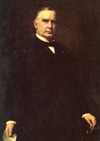 Now for McKinley:
Now for McKinley:
—In September 1901, the president went to Buffalo to visit the city’s PanAmerican Exposition. After visiting Niagara Falls on the morning of Sept. 6, he returned to the fair to shake hands with the public.
–One of the people in the reception line was Leon Czolgosz. His abbreviated descriptor: anarchist. Call him a nut job with a .32-caliber pistol.
—Czolgosz, who would have changed his name to Lee Charles if he had had an agent, shot McKinley twice: one shot deflected off the president’s breast bone, the other struck him in the abdomen and tore through his stomach.
—McKinley was rushed to the rather poorly equipped hospital on the exposition grounds. Doctors were summoned, and they agreed immediate surgery was necessary to save McKinley’s life. Again, no veterinarians within scalpel’s reach of the presidential wounds. The doctor on the scene deemed most qualified to operate was a gynecologist, Dr. Matthew Mann. Contending with poor lighting in an improvised operating theater, he couldn’t find the bullet that had wounded McKinley,and settled for patching up the obvious damage and closing the president up again without draining the wounded area.
—Despite initial optimism that McKinley would recover, his wounds became infected, he developed gangrene, and he died early on Sept. 14.
So it’s clear my Garfield story is mostly McKinley, with a dash of Garfield and a dollop of outrage: Can you believe they let a veterinarian operate on the president?! One question I have for myself: Where did the fiction come from? I do make up stories occasionally — friends and coworkers will testify to that — but usually for the sophomoric pleasure of tricking someone or to make a point. I usually don’t knowingly pass off fanciful historical tales like this as truth; my guess is that, never really having read anything in detail about the Garfield and McKinley killings, I did something fairly common among us humans: jumble some vaguely remembered details together into a plausible narrative (and a narrative all the more entertaining for its improbability).
This all makes me wonder whether I’ve told my version of the Garfield story to someone who knew the actual details and thought, “What a load of crap!”
Like this:
Like Loading...